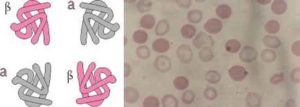
Thalassemia is the name of a group of inherited genetic blood disorder, characterized by absent or decreased synthesis of normal haemoglobin, which is a component of red blood cells and it consists of two different proteins: alfa and beta.
The two main types of Thalassemia are called “Alpha” and “Beta” depending on which part of haemoglobin in the red blood cell is lacking.
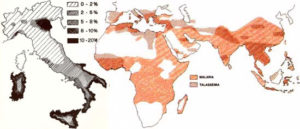
Alfa -Thalassemia is commonly found in Africa, the Middle East, India, Southeast Asia, Southern China and occasionally in the Mediterranean Region. Beta -Thalassemia is mostly found in people of Mediterranean descent, such as Italians and Greeks. On average, there are 3 millions people affected by Beta-thalassemia all over the world.
Only in Italy, the number of patients is roughly 9000.
There are three types of Beta-Thalassemia: Minor, Intermedia and the most severe Thalassemia Major or Cooley¡’s Anemia, in which the reduced or inadequate production of hemoglobin can determine serious damages to the organs.
The complete lack of Beta protein cause a life-treating anemia that requires regular blood transfusions.
These extensive, lifelong blood transfusions lead to iron-overload which must be treated with chelation therapy to prevent early death from organ failure.